10 Questions to Ask During Your Hernia Surgery Consultation in Singapore
Discover when hernia is considered dangerous, the various hernia types...
Home > About Hernia
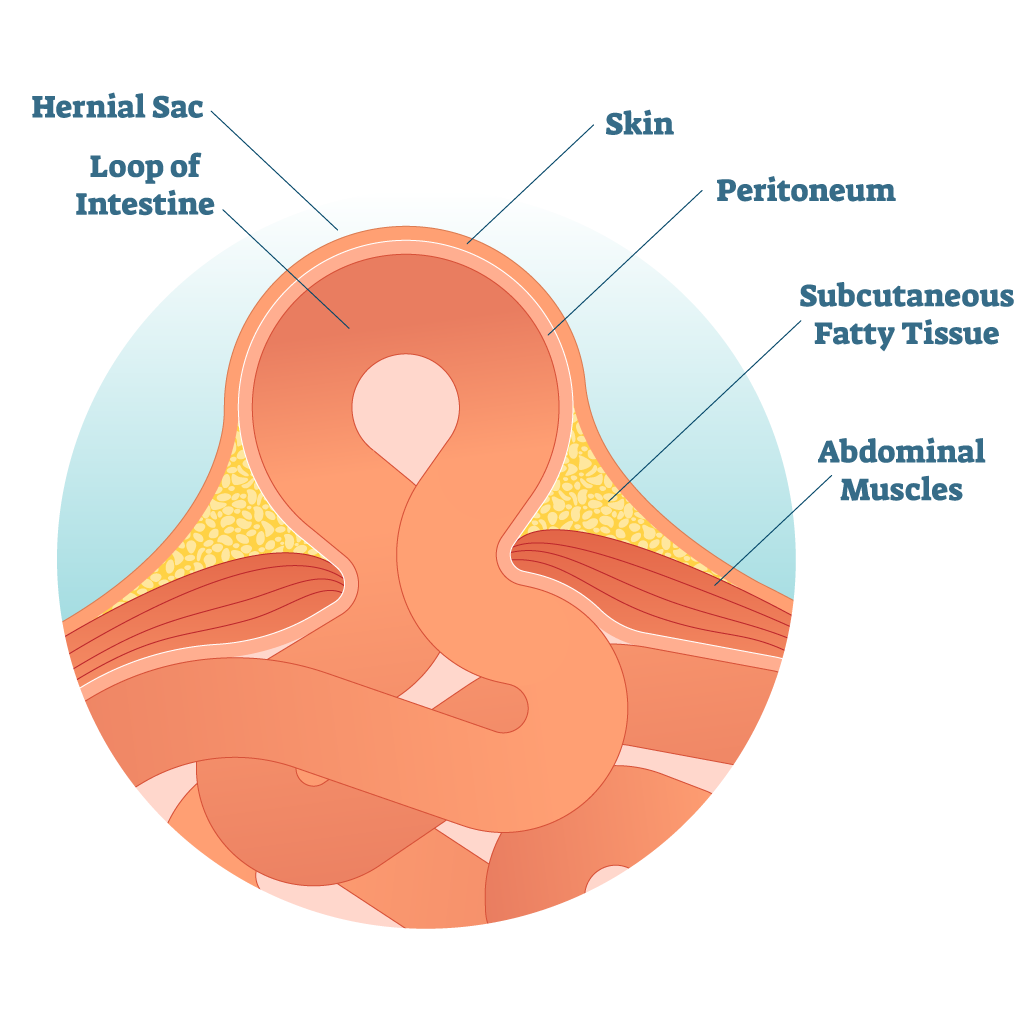
To put things simply, a hernia is a tear in your muscle or tissue that allows part of your insides to protrude out. It can either be the bulging of an internal organ or your intestines. Sometimes the hernia can be very visible, depending on its location and size. Certain activities can worsen the condition, like bending over or lifting heavy objects.
Hernias can occur in different areas of the body, and they are typically classified based on their location. Here are some common types of hernias:
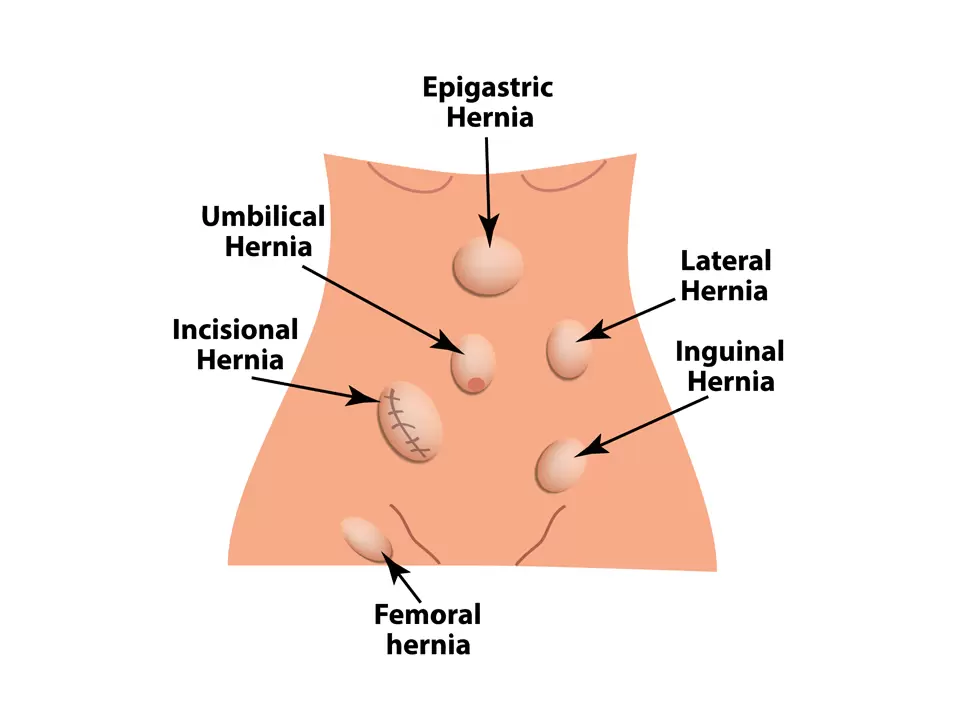
This is the most common type of hernia and occurs in the groin area. It can be further classified into two subtypes.
This type of hernia appears around the navel or belly button and is often seen in infants and young children.
These hernias develop at the site of a previous surgical incision, where the abdominal muscles may have weakened or separated.
This type of hernia occurs just below the inguinal ligament in the upper thigh. It is more common in women and can lead to a painful bulge in the groin.
These hernias occur at any location along the anterior abdominal wall, excluding the inguinal and femoral areas.
Hiatal hernias occur when a portion of the stomach protrudes through the diaphragm and into the chest cavity.
This type of hernia appears in the epigastric region, which is the upper abdomen between the breastbone and the navel.
These hernias occur in the lumbar region of the back and are relatively uncommon.
Lower your chances of complications, see your doctor early and discuss your best treatment options.
If left untreated, your hernia may change in size and become more painful. A portion of your intestine could become trapped in the abdominal wall. This can obstruct your bowel and cause severe pain, nausea, bloating or constipation. In some cases, hernia patients don’t face any symptoms, but if there’s a visible bulge, the likelihood of facing some of these symptoms in the future is high.
An untreated hernia can also put too much pressure on nearby tissues. This can cause swelling and pain in the surrounding area. If the trapped section of your intestines doesn’t get enough blood flow, strangulation occurs.
This can cause the intestinal tissue to become infected or die. A strangulated hernia is life-threatening and requires immediate medical care.

The most common symptom of a hernia is a bulge or lump in the affected area which may not have any symptoms if its small. In the case of an inguinal hernia, you may notice a lump on either side of your pubic bone where your groin and thigh meet. You’re more likely to feel your hernia through touch when you’re standing up, bending down, or coughing. It can disappear when you lie down.
Other common symptoms of an inguinal hernia include:
Discover when hernia is considered dangerous, the various hernia types...
Discover when hernia is considered dangerous, the various hernia types...
Find out all you need to know about groin hernia...
Lower your chances of complications, see your doctor early and discuss your best treatment options.

We understand that hernias are worrying, but they can often be treated early. Here at KYM Surgery, we believe in providing holistic & comprehensive hernia care for all patients.
Hernia Surgery Clinic by KYM Surgery
Copyright © 2024 All rights reserved.