Why Your Groin Hurts When You Cough or Lift (And When to Get It Checked)
Discover when hernia is considered dangerous, the various hernia types...
A hernia occurs when tissue or an organ pushes through a weak spot in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue, creating a noticeable bulge under the skin. Common sites for hernias include the groin (inguinal hernia), abdomen, or near previous surgical scars.
While small hernias may not cause immediate discomfort, most do not heal on their own and can gradually enlarge or become painful. Surgery is often recommended to prevent complications such as strangulation, where the blood supply to herniated tissue is cut off.
The two main surgical methods for repairing a hernia are open repair and laparoscopic (keyhole) repair. Both techniques are effective; the most suitable approach depends on the hernia’s size, type, and the patient’s overall health.
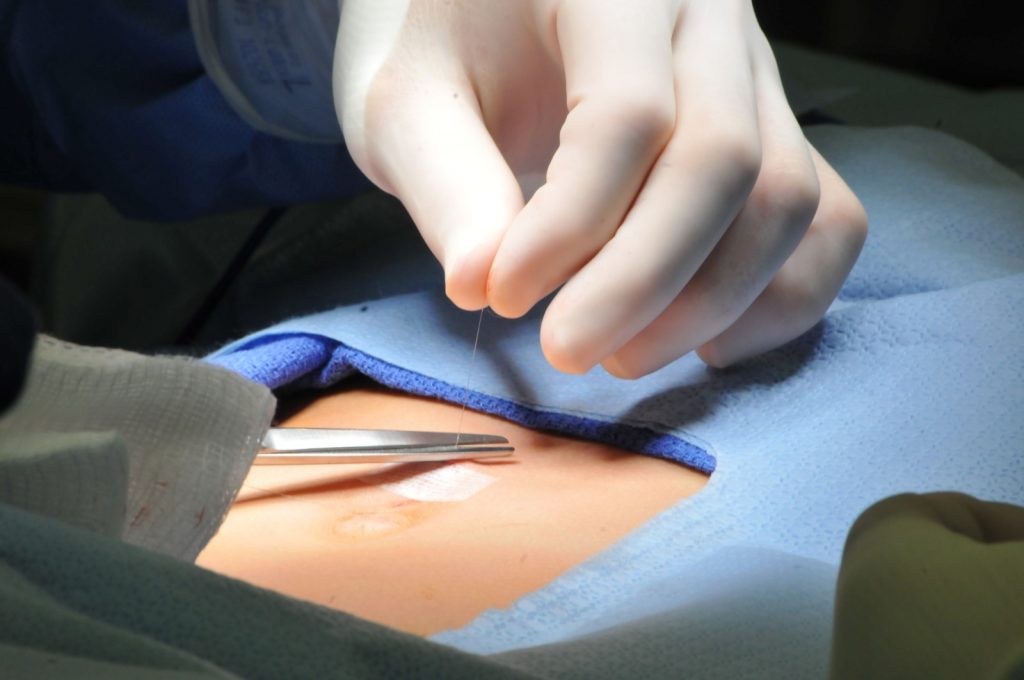
In an open hernia repair, the surgeon makes a single incision directly over the hernia site to access the affected area. The protruding tissue is carefully repositioned, and the weakened muscle wall is reinforced with stitches or with a surgical mesh to reduce the risk of recurrence.
Open repair can be performed under local, regional, or general anaesthesia depending on the case. Patients typically go home the same day or after an overnight stay. Recovery usually takes a few weeks, during which patients are advised to avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activity.
Open surgery may be preferred when:
Laparoscopic hernia repair, also known as keyhole surgery, uses small incisions to insert a camera and fine surgical instruments into the abdomen. The surgeon views the hernia on a magnified monitor and repairs it internally, usually reinforcing the muscle wall with mesh.
Because this technique uses small incisions, patients often experience:
Laparoscopic repair is typically performed under general anaesthesia and may be particularly suitable for:
| Aspect | Open Surgery | Laparoscopic Surgery |
|---|---|---|
| Incisions | One larger incision | Three to four small incisions |
| View | Direct view of hernia site | Camera provides magnified internal view |
| Anaesthesia | Local, regional, or general | Usually general anaesthesia |
| Recovery time | Typically a few weeks | Often shorter, varies by patient |
| Suitable for | Large or complex hernias | Smaller, bilateral, or recurrent hernias |
The duration of hernia surgery depends on the type of procedure, the hernia’s complexity, and whether it is performed as an open or laparoscopic (keyhole) repair.
In most cases, laparoscopic hernia repair takes about 45 minutes to 1 hour, while open hernia repair may take slightly longer, especially for larger or recurrent hernias. Both procedures are typically done as day surgeries, meaning patients can usually go home the same day after a short observation period.
More complex or recurrent hernias may require additional time in surgery and, occasionally, an overnight hospital stay for monitoring. During your consultation, the surgeon will discuss the expected duration, anaesthesia plan, and recovery timeline based on your individual condition.
Not all hernias require immediate surgery, but most will eventually need surgical repair.
Small hernias that do not cause pain or restrict movement may be managed temporarily through watchful waiting, especially if the risk of complications is low. However, hernias typically do not heal on their own, and over time, the opening in the muscle wall may widen, causing the hernia to enlarge or become more uncomfortable.
Your doctor may recommend surgery if:
Early evaluation helps determine whether surgical repair is necessary and allows for planning before complications arise.
There is no single “best” technique for every patient. The decision should be based on a thorough evaluation by a surgeon experienced in both approaches.
Factors considered include:
A detailed consultation helps determine which method offers the safest and most effective outcome for each individual.
At our hernia surgery clinic, we provide a full range of surgical options for hernia repair, including both open and laparoscopic techniques. Every treatment plan is personalised, taking into account the type of hernia, overall health condition, and long-term goals of the patient. We emphasise medical ethics, evidence-based care, and timely post-operative follow-ups to ensure a safe and smooth recovery process.
You should seek immediate medical care if you experience:
These could indicate a strangulated hernia, which requires urgent surgical treatment.
While not all hernias can be prevented, you can reduce your risk by:
Discover when hernia is considered dangerous, the various hernia types...
Discover when hernia is considered dangerous, the various hernia types...
Discover when hernia is considered dangerous, the various hernia types...
Here at KYM Surgery, we believe in providing holistic & comprehensive medical care for all patients.
Here at KYM Surgery, we believe in providing holistic & comprehensive medical care for all patients.